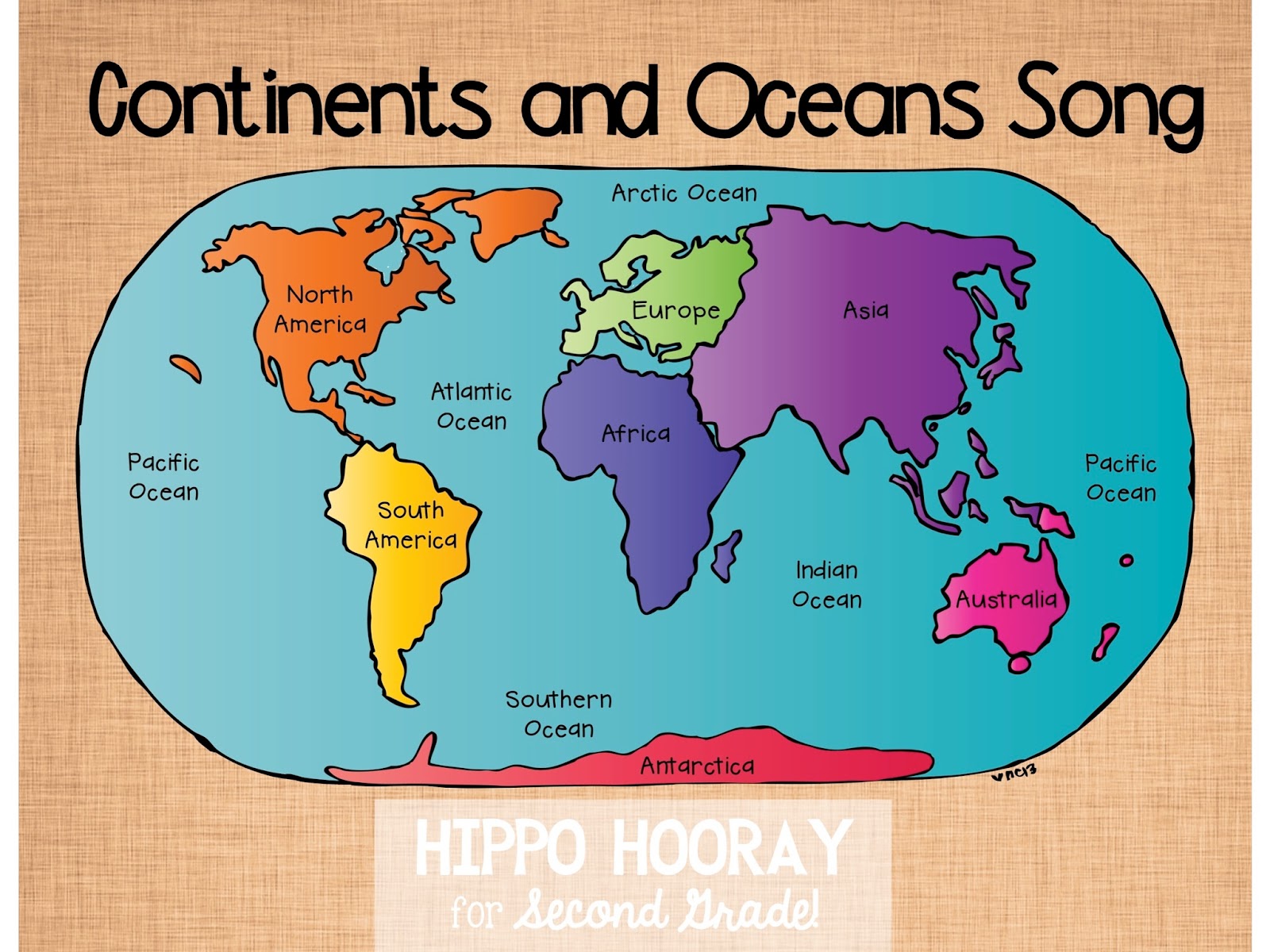
The Earth’s surface is predominantly covered by vast expanses of water, collectively known as oceans. These oceans are not just massive water bodies; they are the lifeblood of the planet, influencing weather patterns, supporting marine biodiversity, and regulating global temperatures. Understanding the different oceans is crucial, as these powerful ecosystems play a pivotal role in sustaining life on Earth. Each ocean has its unique characteristics, from its size and depth to its biodiversity and cultural significance.
Covering over 70% of the Earth's surface, the five major oceans—the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic—are interconnected yet distinct in their own right. From the frigid waters of the Arctic Ocean to the warm currents of the Indian Ocean, these water bodies offer a glimpse into the planet’s diversity. They shape coastal landscapes, provide a habitat for countless species, and are a source of sustenance and livelihood for millions of people. But have you ever wondered what makes each of them unique?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the intricacies of the different oceans, addressing their physical features, ecological importance, and the challenges they face. Whether you’re a student, an environmental enthusiast, or someone curious about the wonders of our planet, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights into the world’s oceans. Let us navigate through their depths and uncover the secrets that lie beneath the waves.
Read also:The Heartfelt Story Behind I Want To Feel The Heat With Somebody
Table of Contents
- The Definition and Role of Oceans
- How Many Oceans Exist?
- What Sets the Pacific Ocean Apart?
- The Atlantic Ocean: A Crossroad of Cultures
- The Indian Ocean and Its Global Impact
- Why Is the Southern Ocean Unique?
- The Arctic Ocean: The Frozen Frontier
- Ocean Currents and Their Role
- Marine Biodiversity in Different Oceans
- How Do Oceans Impact Climate Change?
- Major Challenges Faced by the Oceans
- How Are Oceans Protected?
- Oceans and Human Civilization
- Frequently Asked Questions About Different Oceans
- Conclusion
The Definition and Role of Oceans
Oceans are vast bodies of saline water that cover approximately 71% of the Earth’s surface. They are integral to the planet's ecosystem, serving as a reservoir for heat and carbon dioxide while supporting an immense variety of marine life. Oceans are also crucial for the water cycle, as they contribute to precipitation through evaporation.
Besides their ecological importance, oceans are vital for human survival and economic activities, such as fishing, transportation, and energy production. They also serve as a source of inspiration, recreation, and cultural significance for societies worldwide.
How Many Oceans Exist?
While historically there were four recognized oceans—the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic—geographers now acknowledge a fifth, the Southern Ocean. Despite being interconnected, these oceans are distinct due to their geographical boundaries, climatic conditions, and ecosystems. Together, they form what is sometimes referred to as the "world ocean."
What Sets the Pacific Ocean Apart?
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean, covering more than 63 million square miles. It stretches from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bordered by Asia, Australia, and the Americas. With an average depth of 12,080 feet, it also holds the deepest point on Earth—the Mariana Trench.
Physical Features
The Pacific Ocean contains numerous islands and archipelagos, including Hawaii, Fiji, and the Philippines. It is also home to coral reefs, seamounts, and underwater volcanoes, making it a hotspot for geological and ecological research.
Economic and Cultural Significance
The Pacific Ocean plays a crucial role in global trade, as it connects major economies like the United States, China, and Japan. Additionally, it has rich fisheries and abundant natural resources, including oil and gas reserves.
Read also:Does Amazon Do Price Match A Detailed Guide To Understanding Amazons Pricing Policies
The Atlantic Ocean: A Crossroad of Cultures
The Atlantic Ocean, the world’s second-largest ocean, has been a bridge between continents for centuries. It spans from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bordered by the Americas, Europe, and Africa.
Historical Importance
Known for its historical significance, the Atlantic has been a route for exploration, colonization, and trade. The transatlantic slave trade and the Age of Exploration are pivotal events tied to this ocean.
Modern-Day Relevance
Today, the Atlantic Ocean remains a vital route for international trade and travel. It also supports diverse marine life, such as whales, dolphins, and sea turtles.
The Indian Ocean and Its Global Impact
The Indian Ocean, the third-largest ocean, is known for its warm waters and strategic location. It is surrounded by Asia, Africa, and Australia and connects to the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans through narrow straits.
Geopolitical Importance
Due to its location, the Indian Ocean is a critical route for oil transportation and global commerce. It also hosts important naval bases and shipping lanes.
Environmental Challenges
Despite its significance, the Indian Ocean faces challenges like overfishing, plastic pollution, and climate change. Conservation efforts are essential to preserve its unique ecosystems.
Why Is the Southern Ocean Unique?
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, encircles Antarctica and is the newest addition to the list of oceans. Its cold waters and strong currents make it a distinct and vital part of Earth's climate system.
Ecological Significance
This ocean supports unique marine life, including krill, penguins, and seals. It also plays a crucial role in regulating global temperatures by absorbing carbon dioxide and heat.
Scientific Research
The Southern Ocean is a hub for scientific research, particularly in understanding climate change and ice dynamics. Research stations in Antarctica often focus on studying its waters and ecosystems.
The Arctic Ocean: The Frozen Frontier
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest ocean, located around the North Pole. Despite its size, it is a critical component of Earth's climate system and supports unique wildlife.
Challenges Due to Climate Change
Melting sea ice and rising temperatures threaten the Arctic Ocean and its ecosystems. These changes also have global implications, such as rising sea levels and altered weather patterns.
Indigenous Communities
Indigenous peoples, like the Inuit, have lived around the Arctic Ocean for centuries. Their traditional knowledge and sustainable practices are invaluable for conservation efforts.
Ocean Currents and Their Role
Ocean currents are the continuous movement of water driven by factors like wind, salinity, and temperature. These currents play a crucial role in regulating climate, transporting nutrients, and supporting marine life.
Types of Currents
- Surface Currents: Driven by winds and affecting the upper layers of the ocean.
- Deep Currents: Caused by differences in water density and temperature.
Marine Biodiversity in Different Oceans
Oceans are home to an incredible diversity of life, from microscopic plankton to massive whales. Each ocean hosts unique ecosystems, such as coral reefs in the Pacific and seagrass meadows in the Indian Ocean.
Threats to Marine Life
Overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution are significant threats to marine biodiversity. Protecting these ecosystems is essential for maintaining the health of the oceans.
How Do Oceans Impact Climate Change?
Oceans absorb about 30% of the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities, helping to mitigate climate change. They also store heat, which influences weather patterns and global temperatures.
Challenges of Ocean Warming
However, rising ocean temperatures and acidification pose serious risks to marine life and coastal communities. Addressing these challenges requires global cooperation and innovative solutions.
Major Challenges Faced by the Oceans
Oceans face numerous challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Addressing these issues is crucial for preserving marine ecosystems and ensuring the sustainability of ocean resources.
Plastic Pollution
Plastic waste is one of the most pressing problems, with millions of tons entering the oceans each year. This pollution threatens marine life and ecosystems.
Overfishing
Overfishing depletes fish stocks and disrupts marine food chains. Sustainable fishing practices are essential to combat this issue.
How Are Oceans Protected?
Efforts to protect oceans include establishing marine protected areas, enforcing fishing regulations, and reducing pollution. International agreements, like the Paris Agreement, also address climate change’s impact on oceans.
Oceans and Human Civilization
Oceans have been integral to human civilization, serving as routes for trade, exploration, and cultural exchange. They also provide resources that sustain livelihoods and economies.
Frequently Asked Questions About Different Oceans
1. What are the five different oceans?
The five oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans.
2. Why is the Pacific Ocean the largest?
The Pacific Ocean covers the most extensive area because it spans vast distances across the Earth, from the Arctic to the Southern Ocean.
3. What is the role of oceans in climate regulation?
Oceans regulate climate by absorbing heat and carbon dioxide, influencing weather patterns and global temperatures.
4. Why is marine biodiversity important?
Marine biodiversity supports ecosystem balance, provides food and resources, and contributes to climate stability.
5. What are the main threats to oceans?
The main threats include pollution, overfishing, habitat destruction, and climate change.
6. How can individuals help protect oceans?
Individuals can reduce plastic use, support sustainable seafood, and participate in ocean conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
The different oceans of the world are more than just water bodies; they are the lifeblood of our planet. Each ocean, with its unique characteristics, contributes to the Earth's ecological balance, supports diverse marine life, and provides invaluable resources for humanity. Understanding their importance and addressing the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring a sustainable future. By working together, we can protect these vital ecosystems for generations to come.